1950s
Antennas at this time were simple and only covered radio reception functions.
Lock Antenna



Features
Lock Antenna, which can be hidden in the car body, were developed based on the founder’s experience of having the other type of antenna on his personal car broken.
Mounting Position
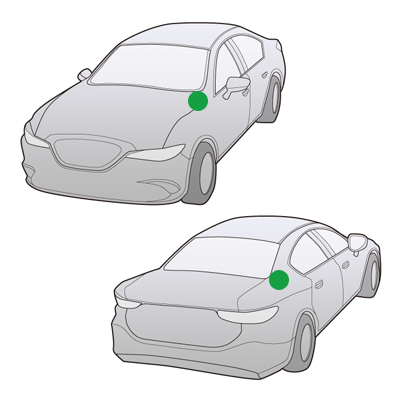
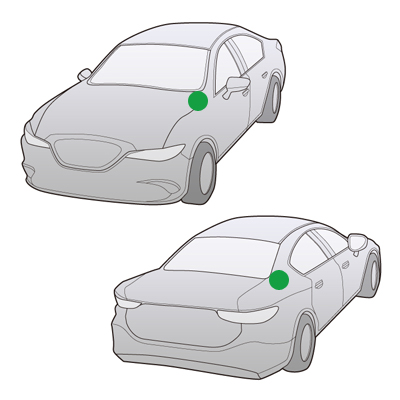
1960s
Motorized Antenna
 Later Model (1990s)
Later Model (1990s) Early Model (1960s)
Early Model (1960s)
Features
A motorized antenna extends and retracts in conjunction with car radio unit so there is no need to manually pull out the antenna. At this time, it was developed for high-end cars.
Mounting Position
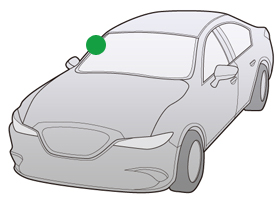
Pillar Antenna
 Later Model (2000s)
Later Model (2000s) Early Model (1960s)
Early Model (1960s)
Features
Pillar antennas were developed on the back of rising demand in radio antennas for trucks. The antennas were modified repeatedly to achieve lighter weight, a more simple design and smaller size, and were adopted by many passenger cars.
Mounting Position
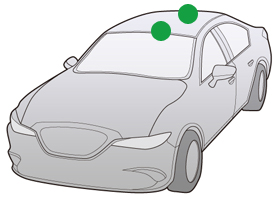
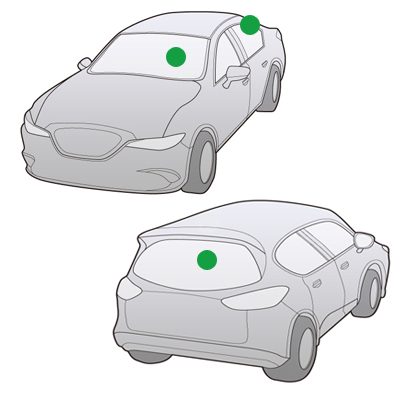
Roof Antenna
 Later Model (1990s)
Later Model (1990s) Early Model (1960s)
Early Model (1960s)
Features
Roof antennas can be designed to support analog radios and digital radios (DAB) etc. They can be composite, supporting multiple media. The antennas come in two types: the collapsible type in which the angle of the rod can be adjusted, or the anchored type in which the rod is fixed.
Mounting Position
1970s
Amplifier for Screen Antennas
 Later Model (2000s)
Later Model (2000s)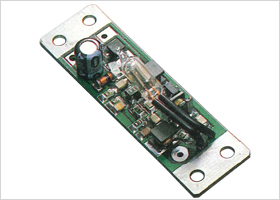 Early Model (1970s)
Early Model (1970s)
Features
The devices amplify signals received by screen type antennas.
The size was reduced, and efficiency of installation was enhanced.
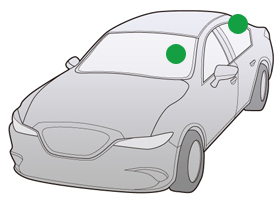
Mounting Position
1980s
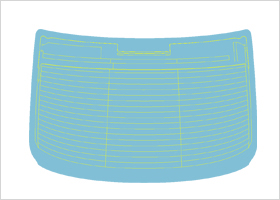
Screen Antenna
 Rear Screen
Rear Screen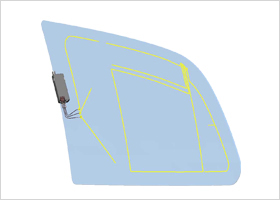 Side Screen
Side Screen
Features
Screen type antennas are embedded into windshield, rear screen or side screen. The antennas excel in design and durability.
Mounting Position
1990s
With the introduction of car navigation systems, satellite radios and ETCs, demand for multi-function antennas increased.
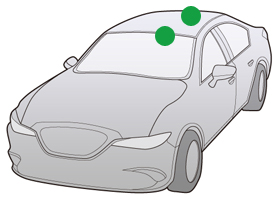
Roof Antenna


Features
Lengths of antennas were reduced significantly to meet the needs in placing emphasis on car design.
The base color of antennas can be adjusted to match that of car body.
They can be composite, covering multiple media in addition to radio.
The antennas come in two types: the collapsible type in which the angle of the rod can be adjusted, or the anchored type in which the rod is fixed.
Mounting Position
2000s
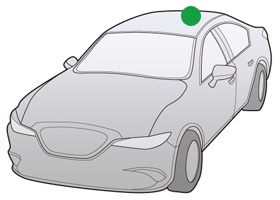
Fin Type Antenna


Feature
Fin type antennas were developed in response to the rising demand of satellite radios and navigation systems, and telematics.
Mounting Position
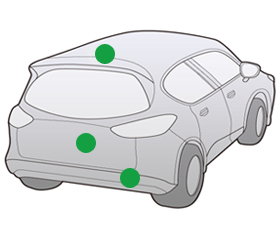
Hidden Type Antenna

Features
Hidden type antennas were developed for cars that place an emphasis on design. The antennas are completely invisible from exterior of cars. The antennas can be built into the roof, trunk lid, spoiler or bumper etc.
They can be composite, covering multiple media in addition to radio.
Mounting Position
2010s
Fin Type Antenna (LPA)

Features
Fin type antennas can support analog radios, digital radios, satellite systems such as GPS, and mobile communication systems with all antennas integrated in one, without affecting car body design.
Early fin type antennas could not combine radio with other media; however, they could be composite with multi-media during this period.
The color of antenna can be adjusted to match that of car body.
Mounting Position
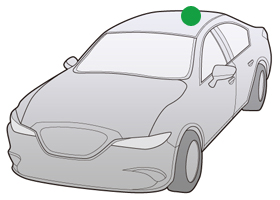
In-Spoiler Type Antenna

Features
The antennas do not affect car design. They can be composite, covering multiple media in addition to radio.
Since a spoiler and an antenna are integrated and offered as one module, it is possible to reduce customers’ man-hours used in developing and assembling products.
Mounting Position
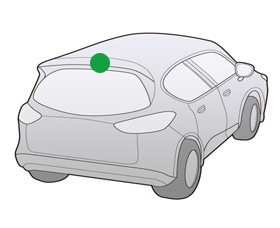
In-Dash Type Antenna

Features
The antennas were developed on the rising demand of integration of antenna for applications, including navigation, telematics and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
They can be composite, covering multi-media, including satellite systems (e.g. GPS), mobile communication systems, DSRC (e.g. ETC).
Mounting Position
Thanks to











